
Heat Staking involves the controlled flow of molten plastic to capture or retain another component, usually of a different material.
Heat Staking is beneficial when joining two parts that consist of different material which cannot normally be ultrasonically welded. Heat Staking is also a cost effective way to bond when simple mechanical retention of one part to another is adequate (as opposed to molecular bonding).
The attachment of metal to plastic is the most commonly used application. A hole in the metal parts is combined with a pre-molded plastic boss. A thermal tip makes contact with the plastic boss and creates localized heat. The light pressure from the thermal tip configuration melts the plastic boss into a predetermined shape. When localized heat is removed, the plastic material solidifies and the different material are fastened together.

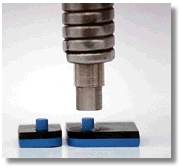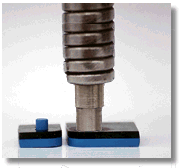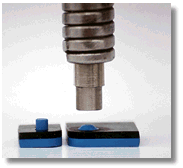




Heat Staking - Ultrasonic Welders - Heatstaking
.
